Imagine you’re a self-employed graphic designer who discovers their ideal house, after which they apply for a mortgage, but major banks reject their application because of income instability and limited credit history. The described situation occurs frequently throughout Canada, particularly among business owners, new immigrants, and people who are rebuilding their financial stability.
The increasing demand for alternative lending options emerges because traditional lending standards have become more restrictive. Private mortgages have become a preferred financing option for Canadians who fail to meet standard banking requirements but demonstrate sufficient assets or income to secure a loan.
What is a Private Mortgage?
Private mortgages represent home loans originated from individual investors and organizations that operate outside traditional banking institutions. These lenders include:
- Individual investors
- Syndicated lenders
- Mortgage Investment Corporations (MICs)
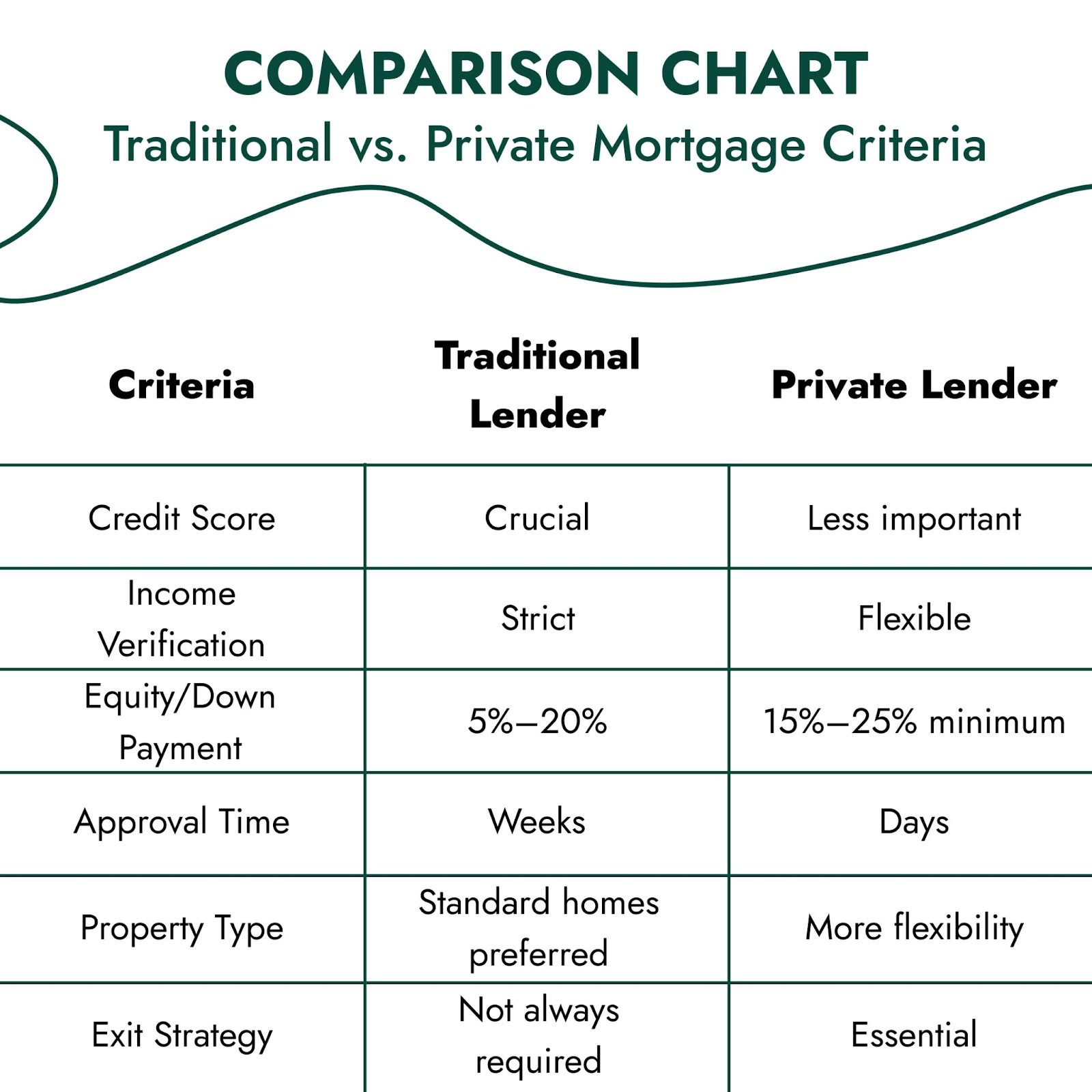
Private lenders operate with different approval procedures than traditional lenders do. Traditional banks base their lending decisions on credit scores, together with income verification and extended employment records. Private lenders base their lending decisions on property value and borrower equity rather than traditional credit score requirements.
Also check out: What Factors Do Mortgage Lenders Consider When Working with Low-Credit Borrowers?
Who are private lenders, and how to get a mortgage from them? Private lenders in Canada are typically:
- Wealthy individuals who use real estate-secured loans to generate returns
- MICs that pool capital from multiple investors to issue mortgages
Private lender mortgages serve three main purposes:
- Bridge financing (between buying and selling properties)
- Self-employed individuals without steady income proof (the requirements for a self-employed mortgage)
- Borrowers with bad credit or recent bankruptcies
These loans have a brief duration, typically lasting one to three years.
Check out Is It Good to Use Private Lenders for Mortgages in Toronto?
How much do private lenders charge in Toronto
Benefits of Using Private Mortgage Lenders
Private home financing provides specific advantages to borrowers who do not meet traditional lending requirements. (Check out How much you can borrow from private mortgage lenders in Toronto)
- Flexible Approval Criteria: Private lenders approve loans through property value and equity assessments instead of traditional credit scores or employment verification.
- Faster Funding Process: The funding process at private lenders takes only a few days to complete, which suits urgent requirements.
- Custom Loan Solutions: Private lenders provide borrowers with personalized loan terms that address their individual needs.
For instance, if a small business owner in Toronto is turned down by a major bank due to inconsistent income, then through a private lender, they can secure a private loan in Canada within a week and successfully purchase a duplex.
Qualification Criteria for Private Mortgages
Private mortgage qualification depends more on your assets and property than on your financial history. Private lenders assess their potential borrowers based on the following criteria:
- Equity or Down Payment: Most private lenders need borrowers to provide 15-25% equity or down payment for loan approval.
- Property Value and Condition: The property functions as security for the loan. The location, together with the property type and condition, determines the eligibility for funding.
- Exit Strategy: The lender needs to understand your plan for loan repayment through property sale, bank refinancing (check out when a mortgage refinancing is needed), or alternative methods.
- Income Proof: The lender requires evidence of your ability to manage loan payments, although they show more flexibility in their requirements.
- Credit History: A bad credit score does not automatically disqualify someone from obtaining a loan, but the lender will evaluate it.
Steps to Qualify for a Private Mortgage in Canada
Here are six main steps to qualify for a private mortgage in Canada.
Step 1: Assess Your Financial Situation: You need to know your monthly income, together with your debt responsibilities, property value, and your ability to handle monthly payments. This will help you set realistic expectations and avoid overextending yourself financially.
Step 2: Determine Your Property’s Equity or Down Payment: Private lenders need borrowers to demonstrate financial investment through 15-25% property value ownership. Having more equity can increase your chances of approval and secure you better loan terms.
Step 3: Gather Necessary Documents: The documents you need include the following list.
- Valid ID
- Income documentation (tax returns, bank statements)
- Property appraisal or purchase agreement
Step 4: Find Private Lenders or Work With a Broker: Through their services, brokers enable clients to meet reliable lenders who provide improved interest rates. They also ensure that you’re dealing with licensed professionals who follow regulatory standards.
Step 5: Get an Offer and Review the Terms: Study the interest rates, together with the loan-to-value ratios and fees that apply. Review the following details before signing:
- Annual interest rate
- Prepayment penalties
- Renewal terms
Step 6: Legal Review and Finalization: A real estate lawyer should review the contract before registering the mortgage.
Let’s consider a Vancouver-based investor who needs funds to close a property deal fast. Within 10 days, they can qualify for a private mortgage and receive funding thanks to a solid exit strategy and a 30% down payment.
Risks and Downsides to Consider
Private mortgages provide fast access to funding, yet they present several trade-offs to borrowers.
- Higher Interest Rates and Fees: The interest rates for private mortgages range from 7% to 15%, and borrowers must pay extra fees to lenders and brokers.
- Shorter Loan Terms: Private mortgages typically have a duration of 1-3 years, which means borrowers need to either refinance their property or pay off the loan when the term ends.
- Limited Regulation: Private lenders operate without federal regulatory oversight, but they must comply with provincial bodies such as the Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA) in Ontario.
- Risk of Foreclosure: Lenders may start foreclosure proceedings if you are unable to repay or refinance.
Are private mortgages regulated in Canada?
There is little regulation of private lenders. Working with licensed professionals is essential, but the Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA) and Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) provide some oversight.
“Borrowers should always consult a licensed mortgage broker and lawyer before entering into a private lending agreement.” – Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA)
Check out How Does Private Lending for Mortgage Work in Toronto?
What is the Process of Getting a Mortgage for a Pre-construction Property in Toronto
Can I Finance 100% of the Purchase Price for a Pre-construction Home in Toronto?
When Is the Right Time to Consider a Private Mortgage?
Private mortgages serve their purpose best when conventional financing options become unavailable to borrowers:
- Denied mortgage applications because of non-traditional income or bad credit
- Urgent funding requirements, such as bridge financing or property closing
- Purchasing unusual real estate, such as a cottage or undeveloped land
- Reducing tax arrears or consolidating debt
For instance, if an investor buys a fixer-upper to flip and banks refuse to finance the house due to its poor condition, based on equity and anticipated resale value, a private lender can intervene to finance the project. Having a well-defined plan to sell or refinance is still crucial for exit strategies.
How to Choose the Right Private Mortgage Lender
Your experience depends heavily on selecting the appropriate lender. Consider these factors:
- Credentials and Licensing: Check that the lender has registration with the Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA) as a provincial regulator.
- Transparent Terms: Read all fees, terms, and repayment conditions carefully.
- Reputation and Reviews: Check Google reviews and industry ratings to evaluate the reputation of the lender.
- Responsiveness: A good lender or broker should guide you through the process clearly and quickly.
- Use a Broker: A mortgage broker who has access to private lenders will help you compare offers and achieve better terms.
Red Flags to Avoid:
- No written contracts
- Vague or hidden fees
- No legal disclosure or property appraisal
Private Mortgage vs. Second Mortgage: What’s the Difference?
A private mortgage and a second mortgage present different financial products despite their similar characteristics. Here’s how they differ:
- Private Mortgage: Functions as either a first or second mortgage through non-traditional lenders. The financing option exists for borrowers who fail to meet bank qualification standards.
- Second Mortgage: Represents a loan which takes place after the primary mortgage on the same property. Traditional institutions, together with private lenders, provide financing for second mortgages.
Key Differences:
- Loan Position: Private mortgages can be in first or second position, whereas second mortgages are always subordinate to the first. The position of a private mortgage exists in first or second place, but second mortgages always follow the first mortgage.
- Purpose: The main purpose of private mortgages function as primary funding, while second mortgages help homeowners access their property equity for purposes like renovations and debt consolidation.
- Interest Rates: Second mortgages, especially from private lenders, tend to carry even higher interest rates due to increased risk.
The knowledge of these distinctions enables you to select the appropriate product for your needs. A mortgage broker should be consulted to determine which option matches your objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions About Private Mortgages in Canada
Do you still have unanswered questions about private mortgages? The following answers address several of the most frequently asked questions.
- Can I get a private mortgage with no income?
Private lenders show flexibility, but they need evidence that you can pay monthly installments that could stem from freelance work, rental income, or alternative revenue streams. - How fast can I get a private mortgage?
The approval process, combined with funding distribution, takes between 3-10 days based on lender requirements and documentation submission. - Do I need a broker to access private lenders?
Not necessarily, but a licensed mortgage broker provides essential services by connecting you with better rates while protecting you from dangerous lenders. - Are private mortgage payments reported to credit bureaus?
The payments are usually not reported to credit bureaus, so regular payments will not enhance your credit score. Legal action, including foreclosure, can occur when you miss payments, even though timely payments do not affect your credit score. - Can I refinance a private mortgage into a traditional one later?
Yes, private mortgages serve as temporary financing options for many borrowers who plan to switch to bank loans after fulfilling standard qualification requirements.
Private mortgages in Canada function as a financial rescue for situations where conventional funding options fail to work. Private mortgages provide adaptable financing with quick processing and personalized solutions, yet they involve elevated expenses, together with elevated risk levels.
The key to obtaining a private mortgage involves demonstrating your property value and presenting a solid exit plan while selecting only authorized lenders.
Ready to explore your options? Our experts will create personalized private mortgage solutions while our full range of mortgage services in Canada remains available for your selection.
If you’re considering a private mortgage in Canada, contact us today to learn more about how we can assist you in securing your private mortgage.

